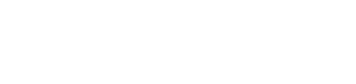eForging: die innovativste, schnellste und schlankeste Fertigungstechnologie
eForging, oder Electro-sinter-forging (ESF), ist ein fortschrittliches Fertigungsverfahren, das Prinzipien der Pulvermetallurgie, des traditionellen Schmiedens und des feldunterstützten Sinterns (FAST) kombiniert. Durch die Überlagerung eines schnellen Hochstromimpulses mit einer schnellen mechanischen Verdichtung ist eForging die innovativste, industriell verfügbare, feldunterstützte Sintertechnologie.
Entwickelt, patentiert und industrialisiert von EPoS Technologies, ermöglicht dieser innovative Prozess eine effiziente und präzise Herstellung einer Vielzahl von Metallen und Metallverbundwerkstoffen und bietet eine hoch flexibles, schnelles und zuverlässiges Fertigungsverfahren.
Advantages
Higher density, better properties
By tapping on high speed and bypassing conventional thermodynamics we can produce full density materials and components with functionalized properties.
Reduced processing time
ESF can significantly reduce the time required to produce high strength and precise parts compared to conventional sintering and forging or machining processes.
High material efficiency
We drastically reduce the amount of matter needed to produce a component reducing the impact on the environment and increasing sustainability.
Low energy consumption
The energy use per weight is significantly lower compared to Additive Manufacturing and methods like Spark Plasma Sintering and Hot Pressing.
More efficient and versatile than Additive Manufacturing. Faster than SPS. Better than press and sinter.
Why we are different?
Unique, Fast, Efficient and Creative.
EPoS Technologies is the pioneer and sole global practitioner of eForging, a groundbreaking manufacturing technology we developed and perfected. With over fifteen years of dedicated research, development, and practical application, we have amassed unparalleled expertise in this innovative process. This deep knowledge allows us to rapidly deliver tailored solutions that help businesses unlock the full potential of eForging, driving efficiency, performance, and competitive advantage.
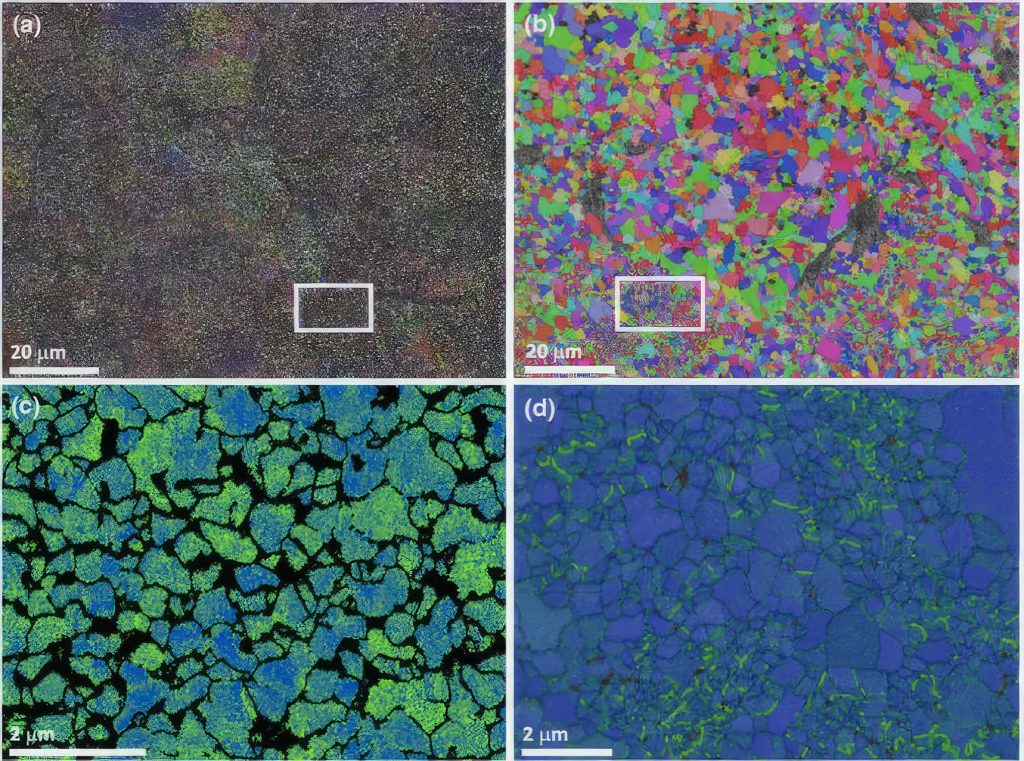
Fig. 1
Figure 1: EBSD maps of (a) and (c) CDS and (b) and (d) SPS Fe-1.5 % Mo components. (c) and (d) Local misorientation maps refer to the regions in the inset of the upper pictures.
Fig. 2
Figure 2: Micro-Hardness Vickers 300 gf versus Density for CDSed (black crossed) ans SPSed (red circles) Fe-1.5%Mo components.
Comparison with Direct Hot Pressing and Spark Plasma Sintering
Not much dissimilar to Spark Plasma Sintering, but much more common in industrial practice due to the simplicity of the system employed, comparisons with Direct Hot Pressing, DHP have been performed on the side of energetic efficiency (“Advancements in single pulse electric current assisted sintering” A.Fais, EuroPM 2013 Congress Proceedings. Cobalt-diamond metal matrix composites for granite cutting were produced with ESF and the energy employed was calculated and compared to DHP.
See in the example aside how ESF employs less than 6% of the energy of DHP.
Direct
Hot
Pressing
#100
20×10.3.8 mm segments
150 kW machine
10 min at full power
3 MJ / segment = 250 Wh / piece
Electro Sintering Forging
#1
20×10.3.8 mm segments
48 kJ charged on bank
–